The EMBO Journal · @embojournal
456 followers · 216 posts · Server sciencemastodon.comProteolytic activation of #angiomotin by #DDI2 promotes #angiogenesis
Cleavage of the scaffold protein AMOT promotes vascular expansion in a manner modulated by membrane localization, poly-(ADP)ribosylation, and ubiquitination
https://www.embopress.org/doi/full/10.15252/embj.2022112900
#angiomotin #ddi2 #angiogenesis
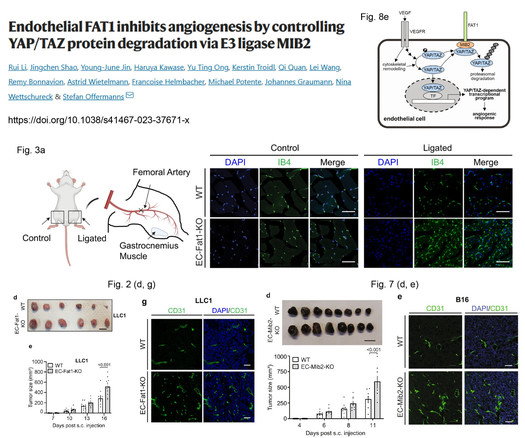
Francoise Helmbacher · @F_Helmbacher
314 followers · 108 posts · Server mstdn.socialBig Congrats 🎉 to Rui Li & collaborators from the lab of Stefan Offermanns at @mpi_hlr
for this great #NatureComms paper showing that FAT1 controls YAP/TAZ degradation via the E3 ligase MIB2 during #angiogenesis.
Happy of my small contribution!
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37671-x
#endothelialcell #taz #yap #fat1 #angiogenesis #naturecomms
Hao Yin · @HaoYin
228 followers · 285 posts · Server qoto.orgEffects of #Aneuploidy on cell behavior & function
Cause:
ROS
DNA replication
mitosis
mechanical confinement
Direct dosage + secondary Effect:
Redox, bioenergetic, proteostasis, Osmosis
Cancer, Aging
Dr Rong Li & Jin Zhu Nature Reviews MCB 2023
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41580-021-00436-9
====
Any evidence on #Aneuploidy in cardiovascular biology?
From Abraham Aviv lab @ATHjournal 2001
Age-dependent aneuploidy & telomere length of the human vascular endothelium
https://www.atherosclerosis-journal.com/article/S0021-9150(01)00506-8/fulltext
Tetrasomy Chr6 Chr16
Loss ChrY
Aneuploidy in cardiovascular diseases?🧐
====
Mice with #SpindleAssemblyCheckpoint protein BubR1 deficiency have a spectrum of vascular defects
Vascular BubR1 1/3
Aging-Associated Vascular Phenotype in Mutant Mice With Low Levels of BubR1
Dr. Jan van Deursen lab @StrokeAHA_ASA 2007
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/01.STR.0000257967.86132.01
=======
Vascular BubR1 2/3
BubR1 Insufficiency Inhibits #NeointimalHyperplasia Through Impaired Vascular #SmoothMuscleCell Proliferation in Mice
Dr. Takuya Matsumoto lab @atvbahajournals 2014
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304737
====
Vascular BubR1 3/3
BubR1 insufficiency impairs #Angiogenesis in aging and in experimental critical limb ischemic mice
Dr. Takuya Matsumoto lab @JVascSurg 2018
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(17)32041-4/fulltext
#NeointimalHyperplasia #aneuploidy #SpindleAssemblyCheckpoint #SmoothMuscleCell #angiogenesis
Development · @Dev_journal
647 followers · 88 posts · Server mstdn.scienceCoronary #EndothelialCells want WT1 as well
A Research Highlight showcasing new work from Marina Ramiro-Pareta, Ofelia Martínez-Estrada & colleagues
Read the full #OpenAccess Research Article, 'Endothelial deletion of #Wt1 disrupts coronary #angiogenesis and #myocardium development', here:
https://journals.biologists.com/dev/article/150/6/dev201147/297331/Endothelial-deletion-of-Wt1-disrupts-coronary
We interviewed the authors, Marina Ramiro-Pareta & Ofelia Martínez-Estrada for our 'The people behind the papers' series:
https://journals.biologists.com/dev/article/150/6/dev201740/297330/The-people-behind-the-papers-Marina-Ramiro-Pareta
#EndothelialCells #openaccess #wt1 #angiogenesis #myocardium #DevBio
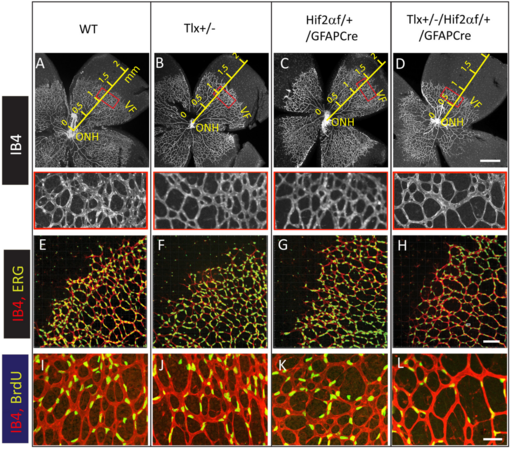
Biology Open · @BiologyOpen
309 followers · 55 posts · Server mstdn.scienceLi-Juan Duan et al. show that #Tailless (TLX) and #hypoxia inducible factor-2α (HIF2α) cooperate to sustain proangiogenic states of retinal #astrocytes in neonatal mice:
#Retina #Angiogenesis #OxygenSensing #Science #BiologyOpen #Biology #AcademicMastodon
#tailless #Hypoxia #Astrocytes #retina #angiogenesis #oxygensensing #Science #biologyopen #biology #AcademicMastodon
Gonzalo · @gcordova
107 followers · 197 posts · Server mastodon.socialJust Published!
"The Implication of miRNA Signature in the Characteristic Features and Diagnosis of Lung Cancer"
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/16833_2023_130
#Cancer #CancerResearch #Angiogenesis #Diagnosis #Biomarkers
#cancer #cancerresearch #angiogenesis #diagnosis #biomarkers
Hao Yin · @HaoYin
221 followers · 248 posts · Server qoto.org#Monocyte deposits VEGF/CXCL12-containing #Migrasome to stimulate CAM #Angiogenesis, as well as reinforce monocyte recruitment
Wonder if this fascinating cascade is also functional in tissue regeneration?😆
Dr. Li Yu lab Nature Cell Bio 2022
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41556-022-01026-3
#Migrasome #monocyte #angiogenesis
European Research Council (ERC · @ERC_Research
746 followers · 1021 posts · Server respublicae.euGetting ready for the weekend? Time to hit the gym!🏃
🆕 discoveries @ETH about how muscles grow could lead to regenerative therapies for conditions like #diabetes & arterial occlusions.
👉 https://bit.ly/3Xka8oD
#angiogenesis #homeostasis
@CORDIS_EU @debocklab @ETH_en
🐦🔗: https://n.respublicae.eu/ERC_Research/status/1616707209936908289
#Diabetes #angiogenesis #homeostasis
Rio Sugimura · @rio_sugimura
172 followers · 773 posts · Server med-mastodon.comRT @HaoYin20@twitter.com
For the #Angiogenesis lovers, read this great #AngioMetabolite story
Endothelial Lactate Controls Muscle Regeneration from Ischemia by Inducing M2-like Mφ Polarization
EC in hypoxic muscle is a major resource of Lactate!
@debocklab@twitter.com @Cell_Metabolism@twitter.com 2020
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1550413120302436
#angiogenesis #angiometabolite
Hao Yin · @HaoYin
221 followers · 233 posts · Server qoto.orgWhat an eye-opening review!👏
Metabolites as signalling molecules
Absolutely a must-read for biology researchers
Dr. Steven Andrew Baker & Jared Rutter Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2023
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41580-022-00572-w
For the #Angiogenesis lovers, read this great #AngioMetabolite story
Endothelial Lactate Controls Muscle Regeneration from Ischemia by Inducing M2-like Mφ Polarization
EC in hypoxic muscle is a major resource of Lactate!
Dr. Katrien de Bock @cell_metabolism
2020
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1550413120302436
So hard to keep updated with the literature, even review🤖
Perhaps need to ask #ChatGPT to how to strategize my reading......
#angiogenesis #AngioMetabolite #chatgpt
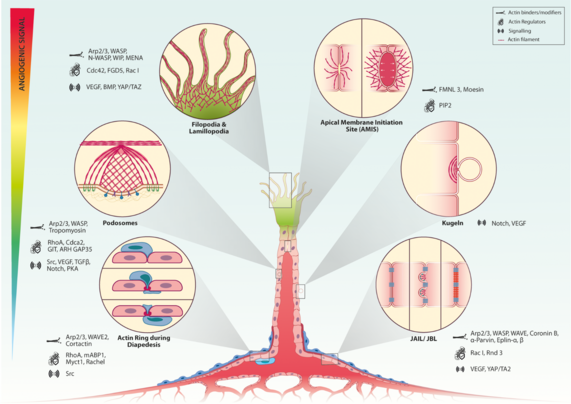
Biology Open · @BiologyOpen
309 followers · 55 posts · Server mstdn.scienceIn this Future Leader #Review, Nidhi Yadunandanan Nair and colleagues discuss how endothelial #actin structures and actin-mediated force generation coordinate the multi-step angiogenic process:
Find out more about how to propose your own Future Leader Review here:
https://journals.biologists.com/bio/pages/reviews
#Angiogenesis #Vasculature #Endothelium #Science #BiologyOpen #Biology #AcademicMastodon
#review #actin #angiogenesis #vasculature #endothelium #Science #biologyopen #biology #AcademicMastodon
Hao Yin · @HaoYin
216 followers · 200 posts · Server qoto.orgStabilizing FOXF1 to treat #AlveolarCapillaryDysplasia
Chemical screening->TanFe
⏬Ubiquitination of FOXF1 via⏬binding to #E3Ligase HECTD1/SHPRH/NEURL1B etc->
Restoring Lung #Angiogenesis of Foxf1+/-🐭
Dr. Vladimir Kalinichenko lab Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2022
https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/10.1164/rccm.202207-1332OC
How FOXF1 impacts #EndothelialCell #Angiogenesis?
As a transcription factor for S1PR1 & VE-Cad😎
An excellent story from Dr. Vladimir Kalinichenko lab @scisignal 2016👇
FOXF1 maintains endothelial barrier function and prevents edema after lung injury
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scisignal.aad1899
Alveolar Capillary Dysplasia with Misalignment of Pulmonary Veins, due to FOXF1 heterozygous mutation, has very complex Lung & ex-Lung vascular phenotypes
A few reads🤠
https://diagnosticpathology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13000-020-00972-6
https://www.nature.com/articles/jp201494
https://www.nature.com/articles/ejhg2012171
https://www.jpeds.com/article/S0022-3476(04)00647-X/fulltext
#AlveolarCapillaryDysplasia #E3Ligase #angiogenesis #EndothelialCell
Gonzalo · @gcordova
100 followers · 117 posts · Server mastodon.socialJust Published!
"The Effects of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors on Metastasis-Associated Myeloid Cells"
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/16833_2022_91
#Angiogenesis #Metastases #Immunotherapy #Cancer #CancerResearch
#angiogenesis #metastases #immunotherapy #cancer #cancerresearch
Hao Yin · @HaoYin
213 followers · 193 posts · Server qoto.orgATF3+ lung capillary #EndothelialCell proliferates & promotes #AlveolarRegeneration post H1N1 injury #Flu
🫁ATF3 KO EC 14 dpi->
⏬Proliferation
⏫Apoptosis
Altered Angiogcrine🤠🧐 to⏬AT1+AT2 epithelial cells
Dr. Edward E. Morrisey lab bioRxiv 2022
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.10.14.512212v1.full
Reminiscent of the really cool work from Dr. Katrien De Bock @cell_metabolism 2021
#SkeletalMuscle ATF3/4+ Capillary #EndothelialCell, preferably surrounding oxidative myofibers, as a major cellular origin of Exercise-induced #Angiogenesis😎
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1550413121003314
#angiogenesis #EndothelialCell #Skeletalmuscle #AlveolarRegeneration #flu
Theory of Living Matter Group · @TLM_Cambridge
245 followers · 594 posts · Server mstdn.scienceRT @GoetzJacky
🔥🎄 Christmas paper alert🎄🔥
Have you ever wondered how and whether fluids that transport #extracellularvesicles impact their fate ?
We did and we now show that blood flow diverts EVs from #endothelial degradative compartments to promote #angiogenesis 🧵
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.12.19.521008v1
#extracellularvesicles #endothelial #angiogenesis
Hao Yin · @HaoYin
207 followers · 183 posts · Server qoto.orgMEG9/Mirg, a LncRNA in Dlk1-Dio3 cardio-angiocluster, links #DNADamage & #Angiogenesis
⏫by Genotoxic stress
⏬by VEGF/FGF2/Dll4/Jag1
🐭Mirg KO affects s.c. Matrigel vessel stability in a Sex-specific manner
Dr. Cristina Espinosa-Diez & Sudarshan Anand lab bioRXiv 2022
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.12.07.519382v1
Hao Yin · @HaoYin
185 followers · 161 posts · Server qoto.orgSplendid #SciArt by Kristy Red-Horse lab
Endocardial Origin of Coronary #EndothelialCell +Arteriogenesis
A fascinating BMP2+ transitioning e17.5 coronary EC population
How EC & nonvascular BMPs coordinate heart #Angiogenesis😆
Exogenous BMP2 synergizes with VEGF-A⏫endocardial-derived Angiogenic sprouting from e10.5🫀ventricle explants
LDN193189, BMPR inhibitor,⏬endocardial contribution to coronary vascularization
AAV9-cTnt-Bmp2⏫endocardial-derived angiogenesis in neonatal #MyocardialInfarction🤠
Dev Cell 2022 @kristyredhorse
https://www.cell.com/developmental-cell/fulltext/S1534-5807(22)00759-6
#sciart #EndothelialCell #angiogenesis #MyocardialInfarction
Hao Yin · @HaoYin
182 followers · 154 posts · Server qoto.org#Autophagy in🐭#LimbIschemia 1/2
AMPK or Sestrin as potential autophagic regulators
Dr. Mattia Scalabrin & Scott Bowen lab AJP CellPhys 2022
https://journals.physiology.org/doi/abs/10.1152/ajpcell.00174.2022
Which tissue does autophagy occur in (likely #SkeletalMuscle based on Western blot)? And its functional impacts?
#Autophagy in🐭#LimbIschemia 2/2
Evidence on autophagy induced by ischemia/#Hypoxia in #EndothelialCell, and its stimulatory effects on #Angiogenesis
Dr. Joo-Won Jeong lab Cell Death Dis 2020
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41419-020-02849-4
#autophagy #Limbischemia #EndothelialCell #angiogenesis #Skeletalmuscle
Hao Yin · @HaoYin
178 followers · 151 posts · Server qoto.orgApold1, a #EndothelialCell-enriched gene, in pathological #Angiogenesis
#LimbIschemia ⏬Reperfusion (3 dpi🤓)-> An arteriogenic defect?
#Stroke ⏫border zone vascularization at day 21 but not day 7
Tumor ⏫Nonproductive angiogenesis-> more non-perfusable endothelial channels
Apold1 KO⏬EC Proliferation-How😁
@bohaceklab & Katrien de Bock bioRxiv 2022
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.12.02.518829v1
Also very interesting, Apold1 KO->⏫KLF2 & KLF4 in EC
Apold1 is recently identified as an ascending aortic EC-enriched gene (vs descending aorta/carotid artery)
Dr. Thomas Quertermous lab bioXRiv 2022
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.05.18.492517v1.full
Are Apold1 KO mice ready for #Atherosclerosis/#Aneurysm?
#EndothelialCell #angiogenesis #Limbischemia #stroke #atherosclerosis
Joseph P. · @tonic
134 followers · 288 posts · Server qoto.orgTumoral Immune Cell Exploitation in Colorectal Cancer Metastases Can Be Targeted Effectively by Anti-CCR5 Therapy in Cancer Patients
Niels Halama, Inka Zoernig, Anna Berthel, Christoph Kahlert, Fee Klupp, Meggy Suarez-Carmona,Thomas Suetterlin, Karsten Brand, Juergen Krauss, Felix Lasitschka, Tina Lerchl, Claudia Luckner-Minden, Alexis Ulrich, Moritz Koch, Juergen Weitz, Martin Schneider, Markus W. Buechler, Laurence Zitvogel,
Thomas Herrmann, Axel Benner, Christina Kunz, Stephan Luecke, Christoph Springfeld, Niels Grabe, Christine S. Falk, and Dirk Jaeger
Targeting Tumor-Promoting Microenvironment Through CCR5 Blockade in #Colorectal #Cancer #Liver Metastases
#Cancer progression is a process in which cancer cells and #immune cells interact with each other in a way that can lead to the growth and spread of cancer. In #colorectal cancer, when the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, it is called #metastasis and it is very difficult to treat. Treatments such as PD-1/PD-L1 blockade and #chemokine modulation have been successful in modifying the interactions between the immune system and cancer, leading to the rejection or suppression of progression. Cancer cells can also alter the immune microenvironment, leading to #immunosuppression and #immune evasion. In this research paper, the authors studied the microenvironment in #CRC #liver metastases and identified a network of #tumor cells and immune cells that exploit the CCL5-CCR5 axis. They then investigated and characterized the effects of blocking the CCL5-CCR5 axis.
the microenvironment of #liver metastases of #colorectal cancer (#CRC).
the environment induces migration of T lymphocytes, which produce a #cytokine called CCL5. This CCL5 then supports tumor growth and spread by influencing macrophages and #tumor cells. The environment is immunosuppressive and the tumor cells are exploiting the host's #immune cells to their advantage. In other words, the tumor cells are using the host's immune cells to help them grow and spread.
the effects of CCR5 blockade on the #tissue level.
Tumor #cell death and a specific pattern of #cytokine and #chemokine modulation are observed in the #ExplantModel and in #tumor biopsies from a #ClinicalTrial. Macrophages are the key for these anti-tumoral effects, as they produce IFNs and reactive oxygen species which cause tumor cell death. #CCR5 blockade induces a phenotypic shift in the macrophages, which is referred to as a switch from an M2 to an M1 phenotype. This repolarization also reduces levels of CD163+ cells, reshaping the #myeloid cell composition in the microenvironment. The influx of new effector cells due to CCR5 inhibition can shift the effects of CCL5 towards beneficial effects, such as reduction of #immunosuppression , #angiogenesis, and #chemotherapy resistance.
The microenvironment of the invasive margin of #liver metastases.
There was no relevant Th1, Th2, or Th17 #cytokine signature present in any of the samples. However, the authors did find that #chemokines and #macrophage-related cytokines were significantly increased at the invasive margin. Chemokines are molecules that help to attract #immune cells to the area, and macrophage-related cytokines are molecules that help to regulate the activity of #macrophages, which are a type of immune cell. 98% of the CD3+ #lymphocyte s in the resection specimens were positive for PD-1, which is a molecule that helps to regulate the activity of the immune system.
#CCL5 is a protein produced by T cells, which are a type of white blood cell. #CCR5 is a receptor found on metastatic tumor cells, which are cancer cells that have spread from the primary #tumor to other parts of the body. In this research paper, it was found that CCL5 has #pleiotropic tumor-promoting effects on #tumor cells and tumor-associated #macrophage s. This means that CCL5 has multiple effects on both the cancer cells and the macrophages, which are a type of white #blood #cell, that are associated with the #tumor. CCL5 was produced mainly by T cells located at the invasive margin and #peritumoral stroma of metastases, and that CCR5 was dominantly expressed by metastatic tumor cells. CCL5 also had effects on tumor #CellProliferation, invasive tumor #CellBehavior, and increased production of matrix #metalloproteinas es by tumor-associated macrophages. Finally, they found that CCR5 inhibition had an effect on key molecules of #epithelial to #mesenchymal transition ( #EMT ).
The researchers wanted to test the effects of #CCR5 blockade, which is a way of blocking the CCR5 receptor on cells, using a drug called maraviroc. They used human #tumor #explantmodel s, which are samples of #tissue from advanced #CRC patients with #liver metastases. Maraviroc led to morphologically overt tumor #CellDeath in the #explants, which means that the tumor cells died and changed in appearance. The researchers then tested the hypothesis that #macrophage s, (type of white blood cell), were required for the tumor cell death-inducing effects of CCR5 blockade. They used clodronate #liposome s to deplete CD163+ TAMs, ( #macrophage s associated with tumors) and found that combining clodronate with CCR5 inhibition abrogated the immediate tumor cell death-inducing effects of #CCR5 inhibition. This confirmed the role of macrophages in this process. IFN-g induced stromal CD163+ #macrophage #cell death and led to a reconfiguration of the #myeloid cell compartment. Inhibition of macrophage-derived reactive oxygen species could partially block the anti-tumoral effects of CCR5 inhibition. Finally, they tested the effects of CCL5/CCR5 inhibition and found that both a CCL5 neutralizing antibody and a CCR5 blocking #antibody had similar functional effects to maraviroc.
A #ClinicalTrial (MARACON) was conducted to test the effects of a drug called maraviroc on patients with advanced-stage #metastatic colorectal #cancer. The #trial involved taking biopsies of the patients before and after treatment with maraviroc, and the results showed that the drug had beneficial effects on the tumor-promoting #microenvironment and led to objective clinical responses. These responses included induction of central #TumorNecrosis, reduction of tumor cell death, and reduction of key #cytokine s and growth factors that promote tumor growth. The drug was also found to be very well tolerated, with mild elevation of #liver enzymes being the most common side effect. Finally, the trial showed that partial responses were achieved in patients with previously refractory disease.
CCR5 blockade, is a type of #therapy used to treat #cancer.
The MARACON clinical trial, showed that CCR5 blockade had a positive effect on the tumor microenvironment and led to a higher response rate in subsequent chemotherapies. The authors suggest that this effect is not limited to the #liver metastases, but is a systemic feature. They also suggest that the local presence of multiple layers of #immune subversion in cancers depends on the individual tissue, #treatment, tumor type, and the difference between primary #tumor and metastatic lesion. The authors also found that the results of the #ClinicalTrial were in line with the results of a fully human organotypic tumor #ExplantModel, which is a simple model with a straightforward approach. The authors also note that the survival data from the trial is not conclusive due to the limited number of patients, but that the objective treatment responses are very encouraging. They suggest that CCR5 blockade may be a promising approach and needs to be evaluated further scientifically and clinically.
#liver #immune #metastasis #chemokine #immunosuppression #crc #cytokine #tissue #cell #ExplantModel #clinicaltrial #ccr5 #myeloid #angiogenesis #chemotherapy #CellProliferation #CellBehavior #therapy #treatment #chemokines #macrophage #macrophages #lymphocyte #CCL5 #pleiotropic #blood #peritumoral #metalloproteinas #epithelial #mesenchymal #emt #celldeath #explants #liposome #antibody #metastatic #trial #microenvironment #TumorNecrosis #colorectal #cancer #tumor