Santiago Andrés Triana · @repepo
126 followers · 48 posts · Server fediscience.orgDo you work on #fluiddynamics of #planetaryCores /moons/atmospheres or #stars? submit your abstract to our #interdisciplinary session for this year's AGU meeting in San Francisco!
https://agu.confex.com/agu/fm23/prelim.cgi/Session/185760
#AGU23 #InertialWaves #GravityWaves #Asteroseismology #Helioseismology #PlanetaryScience
#IcyMoons #GasGiants
#gasgiants #icymoons #planetaryscience #helioseismology #asteroseismology #gravitywaves #inertialwaves #agu23 #interdisciplinary #stars #planetarycores #fluiddynamics
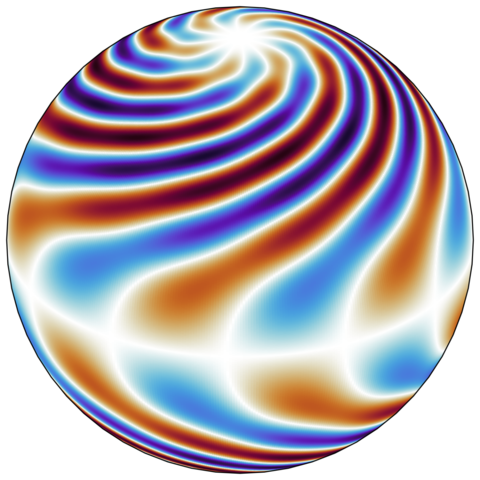
Santiago Andrés Triana · @repepo
319 followers · 352 posts · Server mathstodon.xyzA normal mode (one of the many) of a spinning fluid sphere. #InertialWaves #Physics #FluidDynamics
#fluiddynamics #physics #inertialwaves
Santiago Andrés Triana · @repepo
88 followers · 22 posts · Server mathstodon.xyz#InertialWaves are super weird. It's a rotating #fluiddynamics phenomenon. Their phase speed is perpendicular to their direction of propagation, and they reflect with respect to the #rotation axis, not the reflecting surface!
Their direction determines their frequency: If the #wave vector is \(\mathbf{k} \) and the rotation axis is the vertical 𝑧 then their dispersion relation is
\[ \omega=\pm2\mathbf{\hat k}\cdot \mathbf{\hat z}. \]
Here's an animation I made:
#wave #rotation #fluiddynamics #inertialwaves
Santiago Andrés Triana · @repepo
88 followers · 22 posts · Server mathstodon.xyz#InertialWaves are super weird. It's a rotating #fluiddynamics phenomenon. Their phase speed is perpendicular to their direction of propagation, and they reflect with respect to the #rotation axis, not the reflecting surface!
Their direction determines their frequency: If the #wave vector is \(\mathbf{k} \) and the rotation axis is the vertical 𝑧 then their dispersion relation is
\[ \omega=\pm2\mathbf{\hat k}\cdot \mathbf{\hat z} \] .
Here's an animation I made:
#wave #rotation #fluiddynamics #inertialwaves
Santiago Andrés Triana · @repepo
88 followers · 22 posts · Server mathstodon.xyz#InertialWaves are super weird. It's a rotating #fluiddynamics phenomenon. Their phase speed is perpendicular to their direction of propagation, and they reflect with respect to the #rotation axis, not the reflecting surface!
Their direction determines their frequency: If the #wave vector is \( \mathbf{k} \) and the rotation axis is the vertical \( \hat z \) then their dispersion relation is
\[ \omega=\pm2\mathbf{\hat k}\cdot \mathbf{\hat z} \). Here's an animation I made:
#wave #rotation #fluiddynamics #inertialwaves