Jon Awbrey · @Inquiry
235 followers · 1737 posts · Server mathstodon.xyzFunctional Logic • Inquiry and Analogy • Preliminaries
• https://inquiryintoinquiry.com/2021/11/14/functional-logic-inquiry-and-analogy-preliminaries/
Functional Logic • Inquiry and Analogy
• https://oeis.org/wiki/Functional_Logic_%E2%80%A2_Inquiry_and_Analogy
This report discusses C.S. Peirce's treatment of analogy, placing it in relation to his overall theory of inquiry. We begin by introducing three basic types of reasoning Peirce adopted from classical logic. In Peirce's analysis both inquiry and analogy are complex programs of logical inference which develop through stages of these three types, though normally in different orders.
Note on notation. The discussion to follow uses logical conjunctions, expressed in the form of concatenated tuples \(e_1 \ldots e_k,\) and minimal negation operations, expressed in the form of bracketed tuples \(\texttt{(} e_1 \texttt{,} \ldots \texttt{,} e_k \texttt{)},\) as the principal expression-forming operations of a calculus for boolean-valued functions, that is, for propositions. The expressions of this calculus parse into data structures whose underlying graphs are called “cacti” by graph theorists. Hence the name “cactus language” for this dialect of propositional calculus.
Resources —
Logic Syllabus
• https://oeis.org/wiki/Logic_Syllabus
Boolean Function
• https://oeis.org/wiki/Boolean_function
Boolean-Valued Function
• https://oeis.org/wiki/Boolean-valued_function
Logical Conjunction
• https://oeis.org/wiki/Logical_conjunction
Minimal Negation Operator
• https://oeis.org/wiki/Minimal_negation_operator
#Peirce #Logic #Abduction #Deduction #Induction #Analogy #Inquiry
#BooleanFunction #LogicalConjunction #MinimalNegationOperator
#LogicalGraph #CactusLanguage #PropositionalCalculus
#PropositionalCalculus #CactusLanguage #logicalgraph #minimalnegationoperator #logicalconjunction #booleanfunction #inquiry #analogy #induction #deduction #abduction #logic #Peirce
Jon Awbrey · @Inquiry
231 followers · 1712 posts · Server mathstodon.xyzLogic Syllabus • 2
• https://inquiryintoinquiry.com/logic-syllabus/
Logical Operators
• https://oeis.org/wiki/Logic_Syllabus#Logical_operators
Logical Negation • https://oeis.org/wiki/Logical_negation
Logical NAND • https://oeis.org/wiki/Logical_NAND
Logical NNOR • https://oeis.org/wiki/Logical_NNOR
Logical Conjunction • https://oeis.org/wiki/Logical_conjunction
Logical Disjunction • https://oeis.org/wiki/Logical_disjunction
Exclusive Disjunction • https://oeis.org/wiki/Exclusive_disjunction
Logical Implication • https://oeis.org/wiki/Logical_implication
Logical Equality • https://oeis.org/wiki/Logical_equality
#Logic #LogicSyllabus #LogicalOperator #LogicalConnective
#Negation #NAND #NNOR #LogicalConjunction #LogicalDisjunction
#ExclusiveDisjunction #XOR #LogicalImplication #LogicalEquality
#xor #logicsyllabus #logicalequality #logicalimplication #exclusivedisjunction #logicaldisjunction #logicalconjunction #nnor #nand #negation #logicalconnective #logicaloperator #logic
Jon Awbrey · @Inquiry
78 followers · 249 posts · Server mathstodon.xyz#LogicSyllabus
• https://inquiryintoinquiry.com/logic-syllabus/
This page serves as a focal node for a collection of related resources.
#ExclusiveDisjunction #LogicalImplication
#LogicalConjunction #LogicalNAND
#LogicalDisjunction #Logical#NNOR
#LogicalEquality #Negation
To Be Continued ...
#negation #logicalequality #logical #logicaldisjunction #logicalnand #logicalconjunction #logicalimplication #exclusivedisjunction #logicaloperators #logicsyllabus
Jon Awbrey · @Inquiry
60 followers · 203 posts · Server mathstodon.xyz#DifferentialPropositionalCalculus • 6.2
• https://inquiryintoinquiry.com/2020/03/02/differential-propositional-calculus-6/
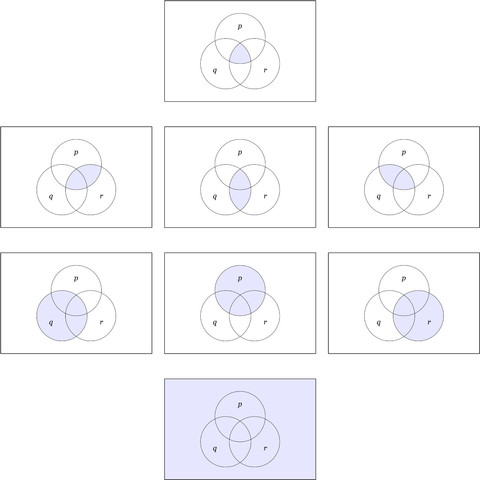
Figure 9. #VennDiagrams for the #PositivePropositions on 3 Variables
• https://inquiryintoinquiry.files.wordpress.com/2020/03/venn-diagrams-e280a2-p-q-r-e280a2-positive-propositions.jpg
Rank 3 (Top). #VennDiagram for the #BooleanProduct or #LogicalConjunction \(pqr.\)
Rank 2. Venn Diagrams for the 3 #BooleanProducts \(pr,\) \(qr,\) \(pq.\)
Rank 1. Venn Diagrams for the 3 #BasicPropositions \(p,\) \(q,\) \(r.\)
Rank 0 (Bottom). Venn Diagram for the #ConstantFunction or the #ConstantProposition \(1.\)
#constantproposition #constantfunction #basicpropositions #booleanproducts #logicalconjunction #booleanproduct #venndiagram #positivepropositions #venndiagrams #DifferentialPropositionalCalculus
Jon Awbrey · @Inquiry
27 followers · 80 posts · Server mathstodon.xyz#DifferentialPropositionalCalculus • 2.2
• https://inquiryintoinquiry.com/2020/02/22/differential-propositional-calculus-2/
Table 6 outlines a #Syntax for #PropositionalCalculus based on two types of #LogicalConnectives, both of variable \(k\)-ary scope.
• https://inquiryintoinquiry.files.wordpress.com/2020/02/syntax-and-semantics-of-a-calculus-for-propositional-logic.png
In the second type of connective a concatenation of propositional expressions in the form \(e_1 ~ e_2 ~ \ldots ~ e_{k-1} ~ e_k\) indicates all the propositions \(e_1, e_2, \ldots, e_{k-1}, e_k\) are true, in other words, their #LogicalConjunction is true.
#logicalconjunction #LogicalConnectives #PropositionalCalculus #syntax #DifferentialPropositionalCalculus