Bose-Einstein-Kondensat · @MWNautilus
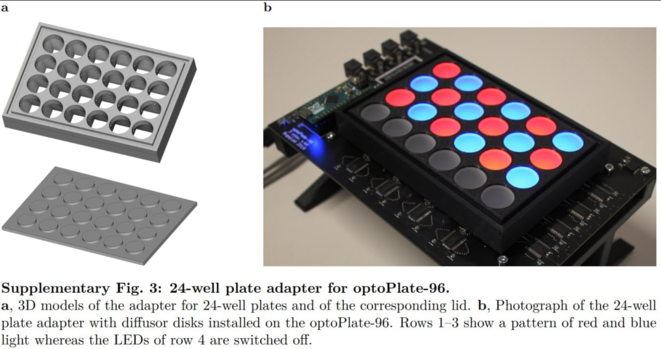
99 followers · 10 posts · Server mstdn.social#optoPlate-96: An #OpenSource #GUI to design high-throughput #optogenetic experiments with the optoPlate-96:
Paper: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-020-0349-x
GitHub: https://github.com/WeberSynBioLab/optoConfig-96
#DIYbio #lab #instruments #Python #Arduino #fluorescence #PlateReader #optogenetics
#optogenetics #platereader #fluorescence #Arduino #Python #instruments #lab #diybio #optogenetic #GUI #OpenSource #optoplate
Bose-Einstein-Kondensat · @MWNautilus
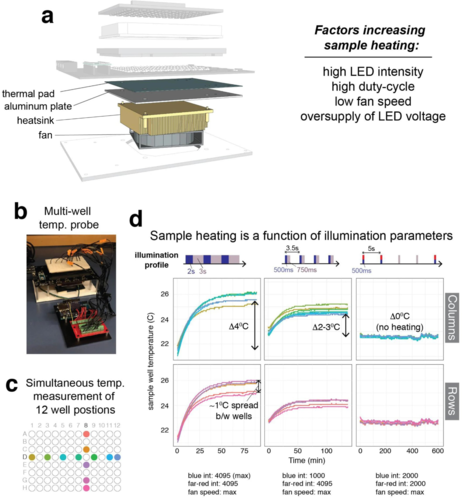
99 followers · 10 posts · Server mstdn.social#optoPlate-96: High-throughput multicolor #OpenSource #optogenetics in #microwell #PlateReader format for $600:
Paper: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-019-0178-y
Web: https://www.bugajlab.com/optoplate
GitHub: https://github.com/BugajLab/optoPlate-96
#DIYbio #lab #instruments #optics #3Dprinting #fluorescence #PlateReader
#fluorescence #3DPrinting #optics #instruments #lab #diybio #platereader #microwell #optogenetics #OpenSource #optoplate
jobRxiv · @jobRxiv
920 followers · 2770 posts · Server mas.toLab Technician
Cleveland Clinic Lerner Research Institute
We are looking for a lab technician who will responsible for rodent handling and behavioral training.
See the full job description on jobRxiv: https://jobrxiv.org/job/cleveland-clinic-lerner-research-institute-27778-lab-technician/?feed_id=49188
#ScienceJobs #hiring #research #behavior, #imaging, #optogenetics, #multiphoton
Clev...
https://jobrxiv.org/job/cleveland-clinic-lerner-research-institute-27778-lab-technician/?feed_id=49188
#multiphoton #optogenetics #imaging #behavior #research #hiring #ScienceJobs
jobRxiv · @jobRxiv
906 followers · 2729 posts · Server mas.toLab Technician
Cleveland Clinic Lerner Research Institute
We are looking for a lab technician who will responsible for rodent handling and behavioral training.
See the full job description on jobRxiv: https://jobrxiv.org/job/cleveland-clinic-lerner-research-institute-27778-lab-technician/?feed_id=48901
#ScienceJobs #hiring #research #behavior, #imaging, #optogenetics, #multiphoton
Clev...
https://jobrxiv.org/job/cleveland-clinic-lerner-research-institute-27778-lab-technician/?feed_id=48901
#multiphoton #optogenetics #imaging #behavior #research #hiring #ScienceJobs
Jonas Wietek :vibing: · @JWietek
328 followers · 180 posts · Server mstdn.science🚨#Optogenetic preprint alert🚨
Check out PdCO:
Light-controlled inhibition of synaptic transmission via the inhibitory #GPCR pathway. #optogenetics #neuroscience
Link:
#optogenetic #GPCR #optogenetics #neuroscience
Poetry News · @haikubot
779 followers · 8237 posts · Server mastodon.cloudBright light for beating
Restoring heart rhythms so fast
Rat tests so promising
#optogenetics #afib #hearthealth #haiku #poetry
The vOICe vision · @seeingwithsound
361 followers · 1013 posts · Server mas.toA #bionic #eye that could #restore #vision (and put humans in the Matrix?) https://www.cnet.com/science/biology/features/a-bionic-eye-that-could-restore-vision-and-put-humans-in-the-matrix/ by @dctrjack on @maxhodak, Science Eye #optogenetics; resolution is one thing, field of view another.
#optogenetics #vision #restore #eye #bionic
Albert Cardona · @albertcardona
1721 followers · 2066 posts · Server mathstodon.xyz“To expand the repertoire of endogenous cellular communication, we developed a synthetic, photon-assisted synaptic transmission (PhAST) system. PhAST is based on luciferases and channelrhodopsins that enable the transmission of a neuronal state across space, using photons as neurotransmitters.”
Porta-de-la-Riva et al. 2023 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41592-023-01836-9
What a fun project and cool finding, and made in #Catalunya to top it off at the Photonic Science Institute.
Combine that with #photopharmacology and neural circuits may be able to dose themselves according to activity patterns.
#neuroscience #PhAST #Luciferase #ChannelRhodopsin #biophotonics #optogenetics
#optogenetics #biophotonics #channelrhodopsin #luciferase #phast #neuroscience #photopharmacology #catalunya
Yvon Jaillais · @YvonJaillais
76 followers · 76 posts · Server tooting.chPoster alert! @J_Cell_Sci
🔬Genetically encoded imaging tools for investigating cell dynamics at a glance🔬
Andrew Plested · @andrewplested
236 followers · 660 posts · Server mstdn.scienceMonumental paper of unnatural amino acid (UAA) mutagenesis in calcium release channels from Isabella Derler and team! Light-activated calcium release in complexes without STIM1 and tons of insights to structure function.
#Chapeau #IonChannels #optogenetics #geneticcodeexpansion
Jonas Wietek :vibing: · @JWietek
321 followers · 164 posts · Server mstdn.scienceRT @DagmarWachten
Want to work as a #postdoc on #optogenetics and tool development, funded by a grant from @ZIM_BMWK - come and join our team at the @IIIBonn @ImmunoSens
LINdoscope · @lindoscope
38 followers · 4 posts · Server masto.ai🔥 DEADLINE EXTENDED! 🔥
Apply until 17 April for our 2-week EMBO #neuroscience practical course on in vivo #imaging (including miniscopes and 2P), #optogenetics, #behaviour, and data #analysis in Magdeburg, Germany: https://meetings.embo.org/event/23-lindoscope#Register
We have fantastic speakers lined up including Karel Svoboda, @TrackingActions, Daniel Dombeck or @antihebbiann.
Travel grants and on-site childcare are available!
https://masto.ai/@lindoscope/110038172926419911
#neuroscience #imaging #optogenetics #behaviour #analysis
Miki Ebisuya · @MikiEbisuya
288 followers · 104 posts · Server mas.toRT @KhammashLab
Optogenetic feedback control of the unfolded protein response (UPR) in yeast can significantly increase the yield of a difficult-to-fold protein. #synbio #optogenetics
https://authors.elsevier.com/a/1gl%7E4_OxxoRmo8
Credit to @MoritzCTSB and @DbenzingerD & thanks to @ETH_en @ETH_BSSE @ERC_Research
LINdoscope · @lindoscope
38 followers · 1 posts · Server masto.aiAre you interested in learning in vivo #calciumimaging and #optogenetics, combined with #behaviour #analysis? We are now accepting applications for our 2-week (4-15 Sep) intensive EMBO Practical Course LINdoscope: Neuroimaging and data analysis. APPLY NOW: https://meetings.embo.org/event/23-lindoscope#Register
#calciumimaging #optogenetics #behaviour #analysis
Prof Hugo Spiers · @hugospiers
834 followers · 525 posts · Server mastodon.sdf.orgRT @obarnstedt
🚨🚨🚨PREPRINT ALERT🚨🚨🚨
We used dual-colour in vivo #two-photon #imaging and #optogenetics to learn what information the #brain’s dorsal #hippocampus sends to #NucleusAccumbens while mice navigated to a learned #reward site. What did we learn…? A🧵1/25 https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.09.531869
#two #imaging #optogenetics #brain #hippocampus #nucleusaccumbens #reward
Jonas Wietek :vibing: · @JWietek
320 followers · 154 posts · Server mstdn.scienceRT @LINdoscope
Are you interested in learning in vivo #calciumimaging and #optogenetics, combined with #behaviour #analysis? We are now accepting applications for our 2-week intensive EMBO Practical Course LINdoscope: Neuroimaging and data analysis. APPLY NOW: https://meetings.embo.org/event/23-lindoscope
#calciumimaging #optogenetics #behaviour #analysis
Oliver Barnstedt · @obarnstedt
310 followers · 24 posts · Server neuromatch.social🔥🔥🔥 PREPRINT ALERT 🔥🔥🔥
https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.09.531869
We used dual-colour in vivo #twophoton #imaging and #optogenetics to learn what information the #brain ’s dorsal #hippocampus sends to #NucleusAccumbens while mice navigated to a learned #reward site. What did we learn…?
While we often like to think of memories as abstract mental states, they actually serve a key role for our survival and that of our ancient ancestors: Remember where there’s a dangerous place and you can avoid it; remember where there’s food and you won’t go hungry.
But how do we go from the memory of a food location to actually approaching it when we’re hungry? We know that dorsal hippocampus (dHPC) is one of the main “memory storage” sites in the brain and important for navigation, but who sits on the receiving end of this information?
Many great colleagues (like @stpntr@twitter.com, @marisosa @lukesjulson@twitter.com,…) have highlighted the role of projections into the nucleus accumbens (NAc), part of the basal ganglia (BG). The BG’s role revolves around action selection, while the NAc largely deals w/ reward processing.
So we know that this dHPC>NAc pathway is needed for linking rewards with locations, but what does the HPC actually tell the NAc? What would we see if we could listen in on their private conversations? As it turns out, this is technically quite challenging because we need to combine cell identity (NAc-projecting or not) with cell activity. To achieve this, we turned to dual-colour two-photon calcium imaging. We labelled NAc-projecting neurons in red and used a pan-neuronal green calcium indicator to see live neural activity in dHPC.
We trained mice to lick in a reward zone on a cued linear treadmill to receive condensed milk which they absolutely love. After 5 days, they expertly slowed down and licked ahead of this reward zone, showing us they learned this space~reward association.
So what happens inside dHPC while mice navigate to this reward location? We hypothesised that either dHPC>NAc cells would be mostly active at the reward zone, or that they would show no spatial bias. As it turned out, neither were true…
Instead, we found that dHPC>NAc neurons showed stronger spatial tuning compared to those dHPC neurons projecting elsewhere (dHPC-). They were also more strongly modulated by the texture cues we provided, suggesting privileged spatial information routing to the NAc.
What about the reward zone though? Many previous studies found place cells clustering near reward zones. When we first looked at the data, we saw little evidence of this (sad emoji), but we noticed some mice performed better than others. When we separated high- from low-success trials, we could see the reward zone being overrepresented by place cells – this effect was particularly pronounced for dHPC>NAc neurons. We could also show that these projection neurons are better at decoding the spatial location ahead of the reward zone.
This suggests that it may be less the sensory environment that determines neural coding but the behaviour with which the mouse engages with it. This is a realisation that has swept across the neurosciences: neural activity in most brain regions seems modulated by behaviour.
Better performance usually goes in hand with deceleration as mice approach the reward zone. So do neurons “care” about speed? We found neurons that were either positively (acceleration) or negatively (deceleration) modulated by speed, as others before us. Interestingly, negatively speed-modulated neurons were overrepresented in the dHPC>NAc population, suggestive of a role in reward approach. To actually obtain the reward, mice not only needed to remember the reward zone but also needed to lick there. Strikingly, we saw that dHPC>NAc neurons became very active around the time of appetitive (but not consummatory) licking. Also, if we zoom in on the activity of individual neurons, we saw a larger proportion of dHPC>NAc neurons tuned to appetitive licking.
Does this mean that dHPC>NAc projections could “guide” the mouse’s lick activity, or do they simply receive a motor signal from elsewhere? To test this, we optogenetically activated excitatory dHPC axons in NAc after mice learned to lick for rewards.
We found that upon stimulation of this projection, mice actually started to engage in appetitive licking. This suggests that dHPC>NAc projections seem to indeed be in the driver’s seat for reward-seeking behaviours.
How can we reconcile this with our previous findings of enhanced spatial and (negative) velocity tuning? Are there separate populations for each of these aspects or do we have “multi-tasker” neurons that can do it all?
Answering this question is not trivial because, as mice approached the reward zone (space), they tended to slow down (speed) and start licking, resulting in a lot of “collinearity” in the behavioural data. To tackle this, we built computational models (GLMs) to predict neural activity based on space, speed, and lick data. We then randomly shuffled each behavioural variable to see if our models got worse. With this approach, we found that indeed dHPC>NAc neurons were more heavily tuned to space, speed, and licking, but we also found many neurons that encoded multiple behavioural features. Indeed, among the dHPC>NAc population, this seemed to be the norm rather than the exception. We tend to cherish those one-on-one relationships like position~activity (place cells) or speed~activity (speed cells), but computationally, such mixed selectivity or conjunctive coding has been suggested to help downstream brain regions to decode action-relevant stimuli. We show that the dHPC routes a strongly conjunctive code to the action-selection relevant basal ganglia (specifically, NAc).
Indeed, we find that conjunctive coding neurons improve the performance of a linear decoder tasked with identifying the reward zone. This raises the possibility that the dHPC routes enhanced conjunctive information to action-specific brain regions such as the NAc.
Overall, we show that dHPC routes an enhanced conjunctive code of space, speed, and lick information to NAc, and that this code can guide goal-directed appetitive behaviour such as licking.
I was fortunate to be joined in this work by @petra_moce and for the unwavering support from @SR_neurostar@twitter.com and @dzne @LIN_Magdeburg@twitter.com, and @IMPRSBrainBehav@twitter.com, as well as funding from @ERC_Research @dfg_public and #sfb_1089. Feel free to send comments and questions! 25/25
Also, if you're coming to NWG in Göttingen next week, please feel free to hit me up at poster ***T25-19A*** Wednesday 1-1:45pm (or write me to meet up).
#twophoton #imaging #optogenetics #brain #hippocampus #nucleusaccumbens #reward #sfb_1089
Tristan Manfred Stöber · @tristanstoeber
258 followers · 74 posts · Server fediscience.orgRT @obarnstedt
🚨🚨🚨PREPRINT ALERT🚨🚨🚨
We used dual-colour in vivo #two-photon #imaging and #optogenetics to learn what information the #brain’s dorsal #hippocampus sends to #NucleusAccumbens while mice navigated to a learned #reward site. What did we learn…? A🧵1/25 https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.09.531869
#reward #nucleusaccumbens #hippocampus #brain #optogenetics #imaging #two
El Duvelle · @elduvelle
556 followers · 2030 posts · Server neuromatch.socialDoing this for #JournalClub soon:
Hippocampal representations of foraging trajectories depend upon spatial context
Did you read it?
Did you like it?
#Hippocampus #CalciumImaging #VR #Joystick #RL #Optogenetics #Micr
#journalclub #hippocampus #calciumimaging #vr #joystick #rl #optogenetics #micr
seeingwithsound · @seeingwithsound
334 followers · 724 posts · Server mas.toImage-dependence of the detectability of optogenetic stimulation in macaque inferotemporal cortex https://www.cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(22)01921-2 #BCI #NeuroTech #optogenetics #neuroscience
More information in the Twitter thread https://twitter.com/RezaAzadi_/status/1625265187338227714 "optogenetic stimulation of high-level visual cortex results in distortions of the concurrent contents of vision"
#neuroscience #optogenetics #neurotech #bci